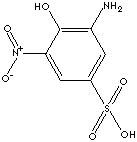
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S.CODE
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
- Michael addition
- Reduction
- Henry Reaction (Nitro-aldol reaction)
- Nef reaction
- O-Alkylation
- Cycloaddition
- Substitution, Elimination, Conversion reaction
- Alkylation, Acylation, and Halogenation
Mononitrophenols are used as intermediates for the synthesis of a number of organophosphorus pesticides, azo dyes, and some medical products as well as their corresponding amonophenols by reduction. some end products derived from mononitrophenols include dyes and pigments, acetaminophen (from p-aminophenol), carbofuran, phosalon (insecticides form o-nitrophenol), parathion,parathion-methyl, fluorodifen (insecticides form p-nitrophenol), nitrofen, bifenox (herbicides form p-nitrophenol), fungicides, and rubber chemicals. Nitrophenol is used as a pH range indicator (colorless at 5 and yellow at 7). Nitrophenol derivatives are used as intermediates for the synthesis of a number of target products.
Sulfonic acid is a compound with general formula RSO2OH, where R is an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a derivative of sulfuric acid (HOSO2OH) where an OH has been replaced by a carbon group or a compound where a hydrogen atom has been replaced by treatment with sulfuric acid; for example, benzene is converted to benzenesulfonic acid (water-soluble). Sulfonic acid has a sulfur atom bonded to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon and bonded also to three oxygen atoms, one of which has been attached to a hydrogen atom. Sulfonic acid is acidic due to the hydrogen atom, stronger than a carboxylic acid. Sulfonic acid is one of the most important organo sulfur compounds in organic synthesis. Sulfonic acids are used as catalysts in esterification, alkylation and condensation reactions. Sulfonates are salts or esters of sulfonic acid. Sulfonic salts are soluble in water. Sulfonic acid and its salts present in organic dyes provide useful function of water solubility and or improve the washfastness of dyes due to their capabiltity of binding more tightly to the fabric. They are widely used in the detergent industry. Alkylbenzene sulfonic acid is the largest-volume synthetic surfactant because of its relatively low cost, good performance, the fact that it can be dried to a stable powder and the biodegradable environmental friendliness. Sulfonate cleaners do not form an insoluble precipitates in hard water. Sulfonic acid salts and esters are intermediates widely used in organic synthesis and particularly phenolic compounds and cation exchange resins. They are synthetic intermediate for a number of biologically active compounds and pharmaceutical candidates such as sulfa drugs.6-Nitro-2-Aminophenol-4-sulfonic acid is used as intermediate for the synthesis of dyes, pigments and other chemical compounds.
APPEARANCE
95.0% min